This article describes the architecture used when you replicate, fail over, and recover Azure virtual machines (VMs) between Azure regions, using the Azure Site Recovery service.
Note
Azure VM replication with the Site Recovery service is currently in preview.
Architectural components
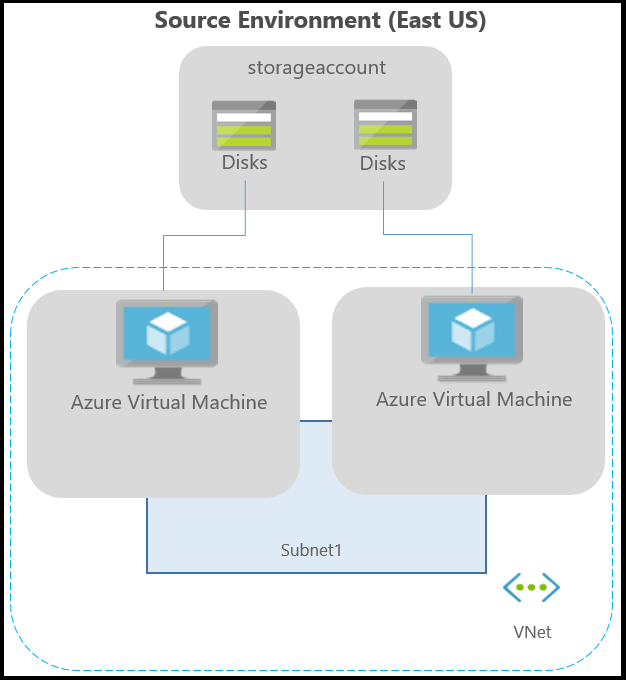
The following graphic provides a high-level view of an Azure VM environment in a specific region (in this example, the East US location). In an Azure VM environment:
- Apps can be running on VMs with managed disks or non-managed disks spread across storage accounts.
- The VMs can be included in one or more subnets within a virtual network.
Azure to Azure replication
Replication process
Step 1
When you enable Azure VM replication, the following resources are automatically created in the target region, based on the source region settings. You can customize target resources settings as required.
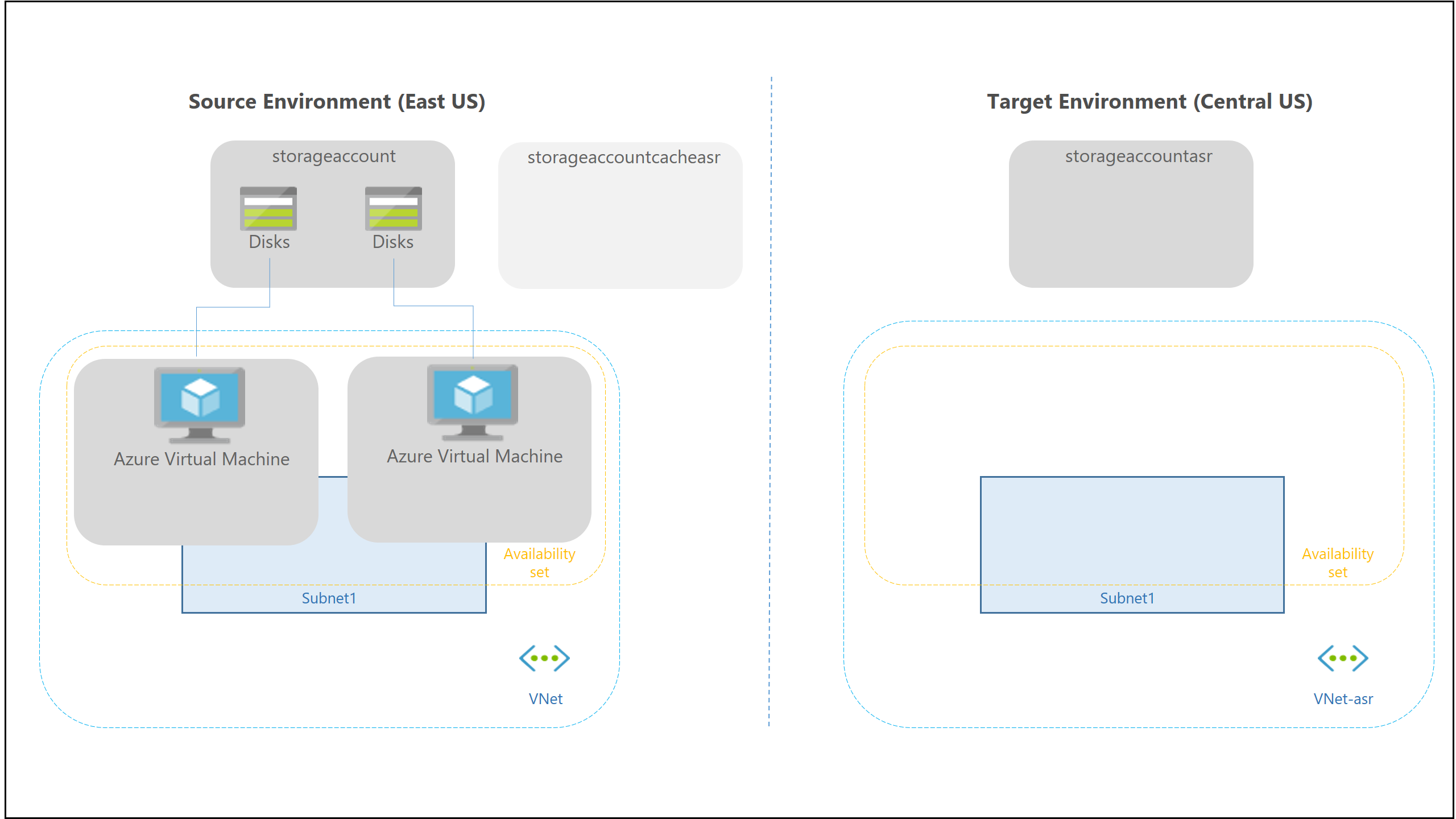
| Resource | Details |
|---|---|
| Target resource group | The resource group to which replicated VMs belong after failover. |
| Target virtual network | The virtual network in which replicated VMs are located after failover. A network mapping is created between source and target virtual networks, and vice versa. |
| Cache storage accounts | Before source VM changes are replicated to a target storage account, they are tracked and sent to the cache storage account in source location. This step ensures minimal impact on production applications running on the VM. |
| Target storage accounts (If source VM does not use managed disks) | Storage accounts in the target location to which the data is replicated. |
| ** Replica managed disks (If source VM is on managed disks)** | Managed disks in the target location to which data is replicated. |
| Target availability sets | Availability sets in which the replicated VMs are located after failover. |
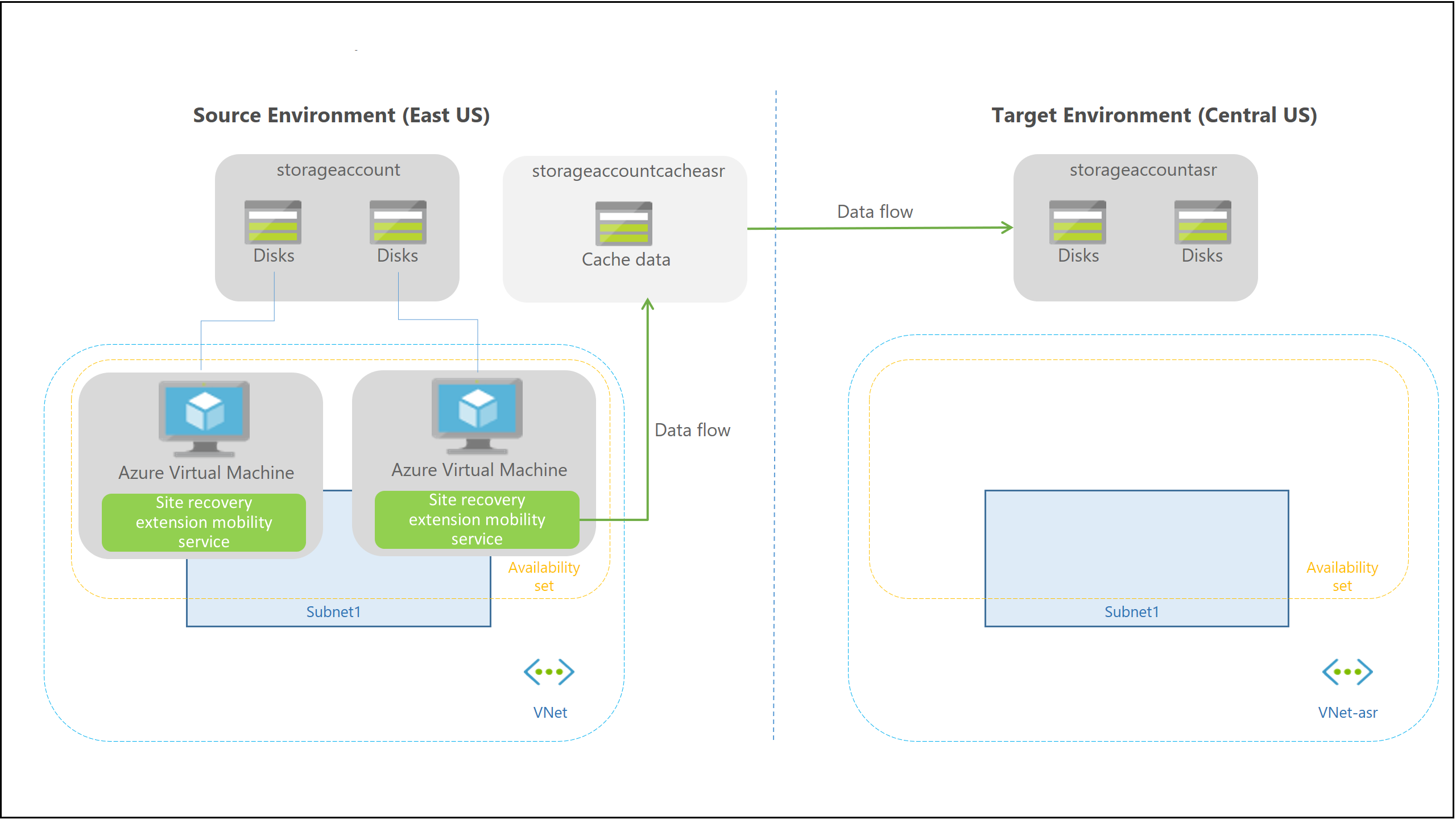
Step 2
As replication is enabled, the Site Recovery extension Mobility service is automatically installed on the VM:
- The VM is registered with Site Recovery.
- Continuous replication is configured for the VM. Data writes on the VM disks are continuously transferred to the cache storage account, in the source location.
Site Recovery never needs inbound connectivity to the VM. Only outbound connectivity is needed for the following.
- Site Recovery service URLs/IP addresses
- Office 365 authentication URLs/IP addresses
- Cache storage account IP addresses
If you enable multi-VM consistency, machines in the replication group communicate with each other over port 20004. Ensure that there is no firewall appliance blocking the internal communication between the VMs over port 20004.
Important
If you want Linux VMs to be part of a replication group, ensure the outbound traffic on port 20004 is manually opened as per the guidance of the specific Linux version.
Step 3
After continuous replication is in progress, disk writes are immediately transferred to the cache storage account. Site Recovery processes the data, and sends it to the target storage account or replica managed disks. After the data is processed, recovery points are generated in the target storage account every few minutes.
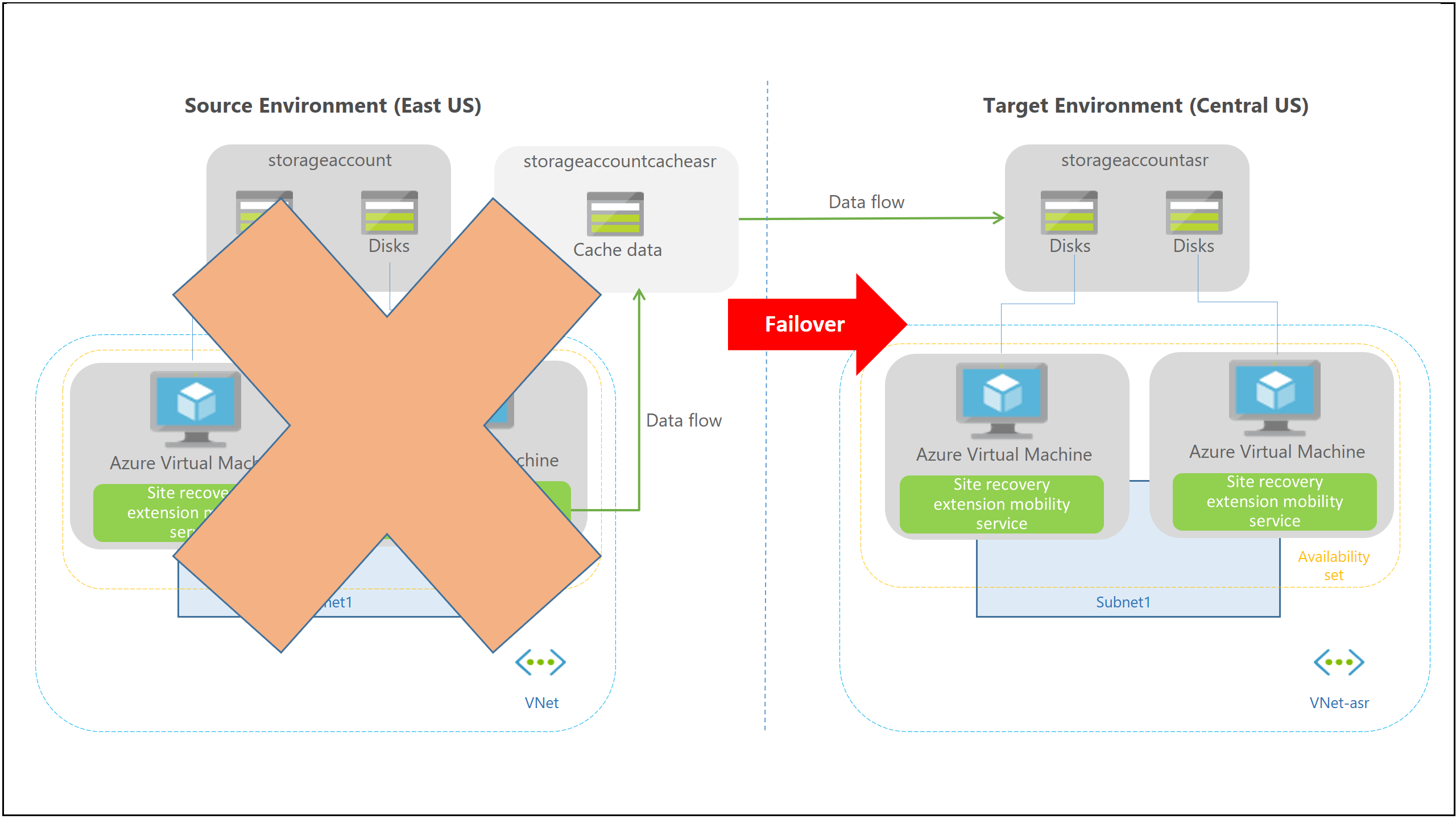
Failover process
When you initiate a failover, the VMs are created in the target resource group, target virtual network, target subnet, and in the target availability set. During a failover, you can use any recovery point.
Next steps
Quickly replicate an Azure VM to a secondary region.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/site-recovery/azure-to-azure-architecture